-
Most common cause of foot pain in athletes. Occurs due to over use and stress on plantar fascia, which can result in tissue fatigue & micro tearing
- Causes plantar fasciitis
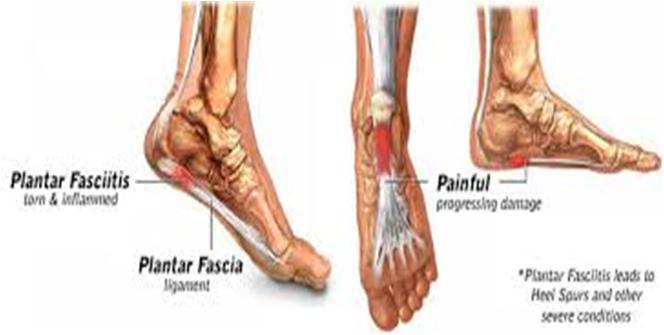 Overuse, due to over training, poor technique, running on hard surfaces or prolonged standing, dancing or runningPredisposing factorsPoor biomechanics – excessive pronation, supination of the subtalar joint or excessive external rotation of the hip joint while walkingShort & tight gastrocnemius & soleus muscles, which predispose foot to pronationImproper footwear that is worn out, too flexible, stiff or does not provide adequate arch support.Weight gain. Including pregnancy, which stresses the plantar fasciaSymptom picture plantar fasciitisCan be unilateral or bilateralSymptoms range from mild to severe. Pain has initial slow onset, with no history of injury or traumaTension is placed on plantar fascia with repeated use & overtime is unable to repair itself & is partially torn away from calcaneus. After an initial period of acute inflammation, chronic inflammation sets in, accompanied by adhesions & fibrosing of the fascia. The plantar fascia thickens with chronic inflammation. Healing is slow as poorly vascularisedPain occurs with the first few steps after non weight bearing (getting out of bed in the morning). Symptoms are worse during pre swing phase of gait cycle an during stair climbing. Pain lessen with activity (30-45mins) then intensifies 2-3 hrs later with continued activity. Usually relieved by restPain Is usually located on antero-inferior surface of calcaneus on weight bearing. It may also extend along medial border of plantar fascia toeards meta tarsal headsPes planus, cavus & Achilles tendonitis are often present. With repeated stress a bone spur may develop on medial aspect of calcaneusTreatment plantar fasciitisAcuteHydrotherapy is cold to affected areaReduce edema if presentReduce sympathetic nervous system firing & painTreat compensating structuresChronicHydrotherapy deep moist heat prior to stretch. Contrast after, increase local circulationReduce sympathetic nervous system firing & painTreat compensating structuresCross fibre frictions used within clients pain toleranceMobilize hypomobile ankle joints
Overuse, due to over training, poor technique, running on hard surfaces or prolonged standing, dancing or runningPredisposing factorsPoor biomechanics – excessive pronation, supination of the subtalar joint or excessive external rotation of the hip joint while walkingShort & tight gastrocnemius & soleus muscles, which predispose foot to pronationImproper footwear that is worn out, too flexible, stiff or does not provide adequate arch support.Weight gain. Including pregnancy, which stresses the plantar fasciaSymptom picture plantar fasciitisCan be unilateral or bilateralSymptoms range from mild to severe. Pain has initial slow onset, with no history of injury or traumaTension is placed on plantar fascia with repeated use & overtime is unable to repair itself & is partially torn away from calcaneus. After an initial period of acute inflammation, chronic inflammation sets in, accompanied by adhesions & fibrosing of the fascia. The plantar fascia thickens with chronic inflammation. Healing is slow as poorly vascularisedPain occurs with the first few steps after non weight bearing (getting out of bed in the morning). Symptoms are worse during pre swing phase of gait cycle an during stair climbing. Pain lessen with activity (30-45mins) then intensifies 2-3 hrs later with continued activity. Usually relieved by restPain Is usually located on antero-inferior surface of calcaneus on weight bearing. It may also extend along medial border of plantar fascia toeards meta tarsal headsPes planus, cavus & Achilles tendonitis are often present. With repeated stress a bone spur may develop on medial aspect of calcaneusTreatment plantar fasciitisAcuteHydrotherapy is cold to affected areaReduce edema if presentReduce sympathetic nervous system firing & painTreat compensating structuresChronicHydrotherapy deep moist heat prior to stretch. Contrast after, increase local circulationReduce sympathetic nervous system firing & painTreat compensating structuresCross fibre frictions used within clients pain toleranceMobilize hypomobile ankle joints
زندگی بدون درد ----- Pain Free Life
ارائه راهکارهای مفید در زمینه فیزیوتراپی

Providing physiotherapeutic guide to gain a Pain Free Life
Archive
- خرداد ۱۳۹۵ (۲)
- ارديبهشت ۱۳۹۵ (۳)
- فروردين ۱۳۹۵ (۲)
Latest Articles
Daily Links



